From solar to electricity.
Generating electricity from solar power is one of the renewable energy applications used to substitute conventional energy sources like oil, coal, and natural gas with other energy sources that are more reliable and environmentally friendly to produce electrical energy from solar energy through solar cells and solar panels.Electricity from solar cells is represented as an electrical current generation in the cells based on the Photovoltaic effect. The photovoltaic is a natural effect that produces an electrical current when sunlight hits the surface of the solar cell made from P-N semiconductor material.
 |
| Solar Cell |
In this article, we will learn how the solar cell generates electricity from sunlight and how to maximize the generated current to achieve maximum benefits. We will also explain in an easy way the definition of each term to make it easy for all.
How is electricity generated from solar?
Before discussing how electricity is generated from sunlight through solar cells and solar panels, let us explain some of the important items in solar cells like semiconductors, P, N, and P-N junction, and the photovoltaic effect.Semiconductor materials.
Semiconductor materials are a type of materials (silicone, germanium, silicon carbide, and gallium arsenide) in between insulators and metals where their conductivity is modified and controlled through physical parameters or factors such as embedded impurities, light, and temperature. Silicon is the most widely used material due to its advantages in manufacturing applications.P, N, and P-N junctions.
P, N, and P-N junctions are semiconductor materials that are doped by other materials to have more negative charges (electrons) and positive charges (holes) to change their physical conductivity. P-type is pure semiconductor materials that are doped by trivalent materials and the N-type is doped by pentavalent material while the P-N is the combination of P and N types.Energy Bands.
In physics, energy bands represent the distribution of solid-state materials’ energy levels where these energy level specifications determine the type of the material metal, insulator, or semiconductor. The main 2 energy bands are the conduction and valence band with an energy gap between them.Photons.
Photons are the basic unit of light that is responsible for the electricity generation from the solar cell. it has electromagnetic energy. the energy of a photon is directly proportional to its wavelength where the higher the wavelength, the lower the photon’s energy.Photovoltaic.
Photovoltaic is the technology for electricity generation by converting sunlight into electricity when the sunlight hits the surface of the solar cell that is made of semiconductor material. The form of the generated power is a flow of current through the solar cell.What are the stages of electricity generation from solar cells?
- When the photon in the sunlight hits the surface of the solar cell, it is absorbed inside the P-n junction (Solar Cell) and hits its electrons. These electrons receive the photon’s energy and start moving through the solar cell.
- The energy transferred from the photons excites the electrons and makes them transfer from the valance band to the higher level of the energy conduction band and become free. It also leads to the creation of the electron-hole pair.
- The movement of the electrons which were excited because of the photons’ hitting from the valance band to the conduction band left behind holes. These generated electron-hole pairs are responsible for the generated current inside the solar cell.
- When the P-N junction is formed, the electric field (barrier potential) starts to be built at the contact between them and when it becomes large enough, it prevents the recombination of the electrons in N-type with holes in P-type and keeps them separate and free on each side.
- Holes move to one of the electrodes (the positive terminal) while electrons move to the other one (the negative terminal) generating a flow of electrical current in the P-N junction (solar cell).
- When a load is connected to the solar cells (solar panels), the free electrons and free holes find their pass through the external circuit as a form of electrical current where a metal grid on the surface of the solar cell collects these electrons and holes.
- Suppose there are some photons for any reason not absorbed in the semiconductor materials. In that case, the anti-reflection material used in the solar cell/solar panels prevents the photons' reflection to increase the chance of reabsorption again inside the solar cell which increases the generated current and increases the efficiency.
What are the properties of the solar cell?
A typical commercial solar cell produces about 3.819 (Pmax/W), 0.29 (Vmax/V), and 0.09 (Imax/A). the efficiency is about 20% on average at the standard test conditions (STC). The STC are 1000 W/m2 solar irradiance, AM1. 5 air mass, and a cell temperature of 77°F(25°C).Solar Panels.
Solar panels are a combination of solar cells that are connected in series to form the solar panels. The output power, voltage, and Amps of the solar panel are determined based on the number of solar cells. Temperature and irradiance of the solar cells significantly affect the efficiency (output of the solar panels.The solar panels' anatomy.
As shown in the below figure, the standard structure of the fabricated solar panel from outer to inner components are: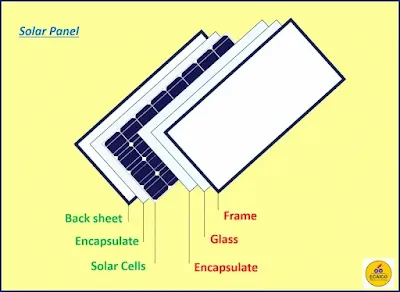 |
| Solar Panel Construction |
- Frame.
- Glasses.
- Encapsulant.
- Solar cells.
- Encapsulant.
- Back sheet.
- Junction Box.
summary.
Converting solar energy into electricity by using solar cells and solar panels based on the photovoltaic effect is very important and has many advantages in the field of electricity generation out of conventional energy sources like coal, gas, and oil.The electricity generation from solar energy passes through 7 steps to get the full generated current. These steps can be reviewed as absorption, excitation, generation of electron-hole pairs, collecting of electron holes, and finally preventing the reflection of the photons to increase the harnessed current from sunlight.
